Dr. Matt Egan



In the 80's hair restoration surgery as a hair loss solution evolved dramatically, as the large punch grafts were gradually replaced with a more refined combination of mini and micrografts. This "combination mini micrografting" hair transplantation procedure no longer used the punch to extract the bald resistant grafts. Rather a strip of bald resistant hair was surgically removed from the back of the head and then trimmed into mini and micrografts.
Typically the minigrafts (4-8 hairs) were used to create fullness and density, while the one, two, and three hair micrografts were used to create a refined and feathered hairline in front. This combination procedure also normally used more grafts, several hundred grafts per session, rather than the approximately 50 to 200 large grafts of the original punch graft procedure.
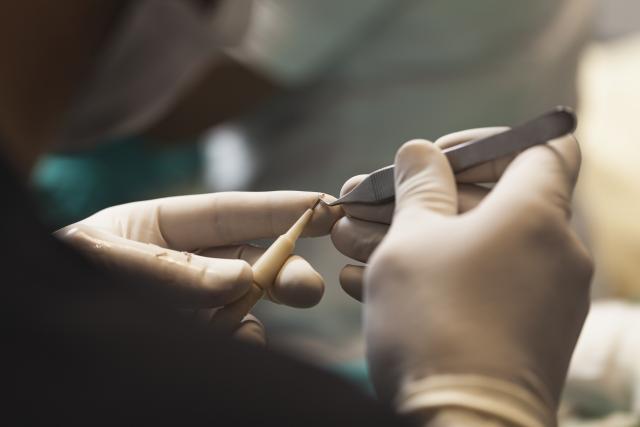
The 90's saw the gradual introduction of a very refined surgical procedure hair loss solution now known as "follicular unit hair transplantation" or "FUT". This exacting and labor intensive procedure transplants hairs in their naturally occurring one, two, three, and four hair "follicular unit groupings" in which they grow naturally.
To create such natural follicular unit grafts, which mimic the way hair grows naturally, typically requires the use of high powered magnification. Such magnification enables the surgical technicians to properly visualize the follicular units in the donor tissue. They are then able to isolate them and cut them into 1, 2, 3, and some times 4 hair follicular unit grafts.
Critical to the ultimate success of the follicular unit hair transplant procedure was the introduction of the binocular microscope by Dr. Bobby Limmer of San Antonio Texas in the late 1980's. Dr. Limmer found that by using the microscope he and his staff were able to successfully isolate and trim the naturally occurring follicular units into individual grafts.
For his part in pioneering the use the microscope in graft dissection and the follicular unit procedure Dr. Bobby Limmer was awarded the "Platinum Follicle Award" by the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery in 1996. Many physicians now fondly refer to him as the "Godfather of Follicular Unit Hair Transplantation".


While Dr. Limmer pioneered the use of the microscope in trimming follicular unit grafts, it was Dr. Robert M. Bernstein, in collaboration with Dr. Bill Rassman, who pioneered and advanced the concept of large sessions of all follicular unit grafting. These large follicular unit sessions enabled patients to achieve both naturalness and density.
Dr. Bernstein, who coined the name "follicular unit hair transplantation", tirelessly advocated for its adoption in ground breaking articles and lectures that are today recognized as benchmarks in the advancement of this procedure. Click to read these ground breaking hair restoration articles and papers.
In recognition of his many contributions in both conceptualizing, pioneering and advocating "follicular unit hair transplantation", Dr. Bob Bernstein was awarded the "Platinum Follicle Award" by the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery.
Over time the merits of this refined but difficult to perform procedure became accepted and the follicular unit hair transplant procedure has become acknowledged by most hair restoration physicians to be the "Gold Standard" for surgical hair restoration. Click here to see video of a Follicular Unit Hair Transplant procedure.
Some feel that hair restoration surgery has evolved to its highest degree now that it relocates hair exactly as it grows naturally. However, even the "Gold Standard" in hair transplantation has continued to evolve by becoming even more "ultra refined".
Today some leading hair restoration surgeons, including all members of the Coalition of Independent Hair Restoration Physicians, perform an ultra refined follicular unit hair transplant procedure using very tiny incisions that enable them to safely "dense pack" tiny grafts when appropriate. This ultra refined follicular unit procedure is a hair loss solution that enables patients to achieve cosmetic density in a given area after only one surgical session.
Childbirth may result in hair loss. It's common for many women to notice hair loss about 3 months after they've had a baby. This too, is caused by hormones. But this is not something to worry about. You see, during pregnancy, hair that normally falls out is kept in by high levels of hormones. Once the hormones have returned to pre-pregnancy levels, this extra hair falls out. The normal cycle of hair growth and loss then begins again.

For many hair loss sufferers, scalp "tinting" solutions are the most effective type of topical concealer. Tinting solutions like COUVRé, also commonly referred to as "masking lotions" or "concealing lotions," eliminate the contrast between thinning hair and the bald scalp by naturally darkening the skin and matching the tone to one's existing hair. By matching bald scalp to an individual's natural hair color, the harsh contrast of thinning hair is eliminated, and a fuller, denser appearance is achieved.
Although several types of masking lotions currently exist, one of the most popular and trusted is COUVRé. However, what makes COUVRé distinct from other masking lotions, or different types of concealers in general? Is COUVRé a quality concealer for both hair loss suffering men and women? Most importantly, what are other concelears users saying, and where can balding individuals purchase their own supply of COUVRé masking lotion?
Unlike comparable "shaker" application products (such as Toppik – a popular topical applicator product from the same makers as COUVRé), COUVRé is a tinted lotion, meant to minimize the contrast between dark, thinning hair and the balding scalp. According to the manufacturers, COUVRé is applied to the scalp using a specialized sponge applicator. Once the masking formula is on the scalp and providing sufficient camouflage, users are instructed to simply style hair normally and go about their day. The manufacturer of COUVRé assert that the application appears subtle, natural, will not appear "greasy or sticky," will not stain clothing or towels, and does not interfere with pores or affect natural hair growth.
According to both the manufacturers and satisfied users, COUVRé offers various benefits over comparable concealer products. First, because the makers of COUVRé are confident in the product, they ensure that, unlike some other concealers, COURVe will create a natural appearance without looking greasy or sticky, and does not clog scalp pores or interfere with existing hair shafts. Because of this, not only is COUVRé useful for those with thinning hair, but also for patients awaiting new growth from hair transplant surgery. What's more, COUVRé does not contain any harmful chemicals, can allegedly withstand perspiration, rain, wind, and even physical contact (such as touching the scalp). COUVRé comes in 8 different colors/tones (to match all hair types) and is equally effective in both male and female hair loss sufferers. Although COUVRé will withstand a variety of situations without smearing or smudging, it easily washes completely away with water and shampoo.
COUVRé Color Chart 
While COUVRé does offer many benefits above other concealer products, its popularity and reputation within the hair restoration community is likely due to several important factors. First, unlike some other concealing products, COUVRé application is both simple and fast. For many individuals, the ability to naturally conceal thinning hair without spending an excessive amount of time "getting ready," is a huge benefit. Furthermore, because COUVRé contains natural ingredients and does not interfere with native or implanted hairs, it is safe to use with other proven hair loss medications (like Rogaine/minoxidil and Propecia/finasteride) and during the new growth phase of hair restoration surgery. Because of its ease of use, effective nature, and ability to conceal hair loss in a variety of situations, COUVRé has become a reputable hair loss treatment and remains popular within the hair restoration community.
To read real reviews on COUVRé alopecia masking lotion from other hair loss suffering men and women, visit our hair loss forum and social community.

Unlike male pattern baldness (MPB) and female pattern hair loss (FPHL), which tends to follow one of the hair loss patterns defined by the NorwoodScale and the LudwigScale, Diffuse Patterned Alopecia (DPA) is characterized by diffuse thinning throughout the front, crown and vertex(crown) with no distinct pattern evident. However, like male and female pattern balding,Diffuse Patterned Alopecia patients typically preserve the stable "permanent zone" on the sides and back of the scalp and may sometimes retain a well-defined hairline. DPA is also a type of hereditary balding condition like and rogenetic alopecia (genetic hair loss).
Diffuse Patterned Alopecia (DPA) can be difficult to diagnose and, particularly in its early stages, may be confused with a similar condition known as Diffused Unpatterned Alopecia (DUPA). While both conditions are characterized by diffuse thinning, DUPA sufferers lack the stable permanent zone necessary for surgical hair restoration.
DPA often responds well to medical hair loss treatments like Propecia (finasteride) and Rogaine(minoxidil) and, due to the preservation of the permanent donor region, many DPA sufferers are candidates for hairrestoration surgery.
It’s essential that hair loss suffering men and women seeking medical and/or surgical treatment for diffuse thinning consult with a skilled and experienced hair restoration physician. Differentiating between DPA and DUPA is critical because Diffuse Patterned Alopecia patients frequently make good hair transplant candidates, whereas DUPA patients rarely do.

 Crinagen is an all natural alcohol-free topical scalp spray clinically backed to reduce the amount of DHT (dehydrotestosterone) in the scalp. It contains no alcohol, and has displayed no side effects. Crinagen is also equally safe for men and women and is most effective in men and women with thinning hair. In addition to blocking scalp DHT, they both are reported nourish the scalp’s hair follicles. Crinagen usually displays its effects on average in five months.
Crinagen is an all natural alcohol-free topical scalp spray clinically backed to reduce the amount of DHT (dehydrotestosterone) in the scalp. It contains no alcohol, and has displayed no side effects. Crinagen is also equally safe for men and women and is most effective in men and women with thinning hair. In addition to blocking scalp DHT, they both are reported nourish the scalp’s hair follicles. Crinagen usually displays its effects on average in five months.
The product's main ingredients are Saw Palmetto, Zinc, and Azelaic Acid. All 3 ingredients are reported to reduce the production of scalp DHT and nourish the scalp's hair follicles.
Crinagen has not been clinically proven nor approved by the FDA. Thus, like Revivogen and Tricomin, Crinagen should be used only after seriously considering proven treatments like Propecia (finasteride) and Rogaine (minoxidil).
Don't expect immediate results. It's recommended to use Crinagen for at least 6 to 12 months before determining its effectiveness. Documenting your progress with bi-monthly photos can help you determine whether or not Crinagen is working for you.
Hair shedding is a common symptom the first few months and a sign that the medication may be working for you. It's crucial to push past this stage with continued use for the recommended period of time.
To date, only surgical hair restoration is proven to grow hair in completely bald areas. You are invited to have a free virtual consultation with one of our prescreened hair restoration physicians.

We know that and rogenetic alopecia or male pattern baldness is by far the most common cause of hair loss, accounting for 95% of hair loss in men and women. But there are a variety of other causes for hair loss in men and women. These include disease, aging, improper hair care, poor nutrition, and stress.
It's a proven fact that medical conditions, as well as treatments and procedures, may lead to hair loss. Many people have experienced sudden and large amounts of hair loss about 3 or 4 months after an illness or a major surgery. Fortunately, this hair loss is usually temporary, and is related to the stress of the illness.
Hair loss may also signal a previously hidden disease,including lupus, thyroid disease or diabetes. Because hair loss may be an early sign, it's a good idea to identify the problem and begin treating it at this time.
Psychological disorders such as Trichotillomaniamay be responsible for self-inflicted hair loss Men and women suffering from this condition pull their own hair out by the roots.
Hair loss may stem from taking certain medicines, but this normally stops once the medication is no longer taken.
Another cause of medical hair loss is hormonal problems. Essentially, having an overactive or under active thyroid gland may cause your hair to fall out. Treating the thyroid disease will usually help this hair loss. Hormones can also cause hair loss if male hormones (androgens), or female hormones (estrogens), are out of balance. However, if the hormone imbalance is corrected, the hair loss should stop.
Did you know that 40% of men have noticeable hair loss by age 35, and 65% by age 60?
Aging is one of the factors necessary for and rogenetic alopecia to occur, along with a genetic predisposition and the presence of hair loss-inducing hormones. Hair loss is dependent on exposing the vulnerable hair follicles to the proper hormones over time.
Isn't it frustrating to see people with thick, full heads of hair treat it so badly? Dyes, bleaching, pigtails -- it all takes its toll on hair.
The chemicals used for dying, tinting, bleaching, straightening or any other hair-altering procedures can lead to hair becoming strained or damaged. Eventually, this hair may even break off.
But it's not any better in the hair salon, as excessive styling that pulls the hair too tightly may also lead to a type of hair loss, called "traction alopecia." As long as this pulling is stopped before the scalp scars, the hair will grow back normally. But be warned, scarring can cause permanent hair loss.
It's also not a good idea to subject your hair to hot oil treatments or the chemicals used in permanents. These may cause inflammation of the hair follicle. This too, may lead to scarring and hair loss.
Researchers have found that some hair loss may be due to insufficient protein or iron in your diet, as well as malnutrition, in general. As effective as "miracle" or "fad" diets sound, they may cause damage. Vitamin deficiencies, as well as certain illnesses related to eating, such as bowel disease or eating disorders, can also cause poor nutrition. These may all cause hair loss.
Stress can be harmful to the entire body, and the hair on our heads is no exception. Regardless of the cause - illness, a traumatic experience, nutritional deficiency - our rate of hair loss may increase.
However, it should be noted that stress-induced hair loss is not a cause of male-pattern baldness. Rather, this type of balding is known as "telogen effluvium." Telogen effluvium is caused when the body senses a problem and diverts its energies there. This results in hair being shed, although it's usually reversible.
Stress affects the hair of men and women differently. It's been foundthat women's hair is more sensitive to stress' effects than men's hair. One possibility is that stress (along with DHT and other things) may facilitate hair loss for women who are genetically predisposed towards it While the cause of genetic female hair lossis a bit of a mystery, women experiencing hair loss are advised to consult a dermatologist or hair restoration specialist to determine its cause Many causes of thinning hair in females are non-genetic and hair loss is often reversible by treating whatever condition is promoting it.

Female hair loss, otherwise known as Female Pattern Baldness (FPB), affects 1 out of every 4 women in the United States. Recent findings have found that the incidence of FPB has been reported to be as low as 8% and as high as 87%. And, it does appear to be as common for women as for men. Most often, menopause is the most frequent time for hair loss in women to become apparent.
For a woman to lose her hair can be even more troubling than for men. A woman with thinning hair is not generally accepted as part of the normal aging process. Society has come to expect a thick, luxurious head of hair as part of the attractiveness in women.
While males and females can both experience thinning hair, they typically do not lose their hair in the same order or appearance.
Typically men observe their hair loss earlier, whereas women will first notice it in their late 20's through their early 40's. Female Pattern Baldness (FPB) is often seen during hormonal changes. These include the use of birth control pills, following childbirth, or during or after the time of menopause.
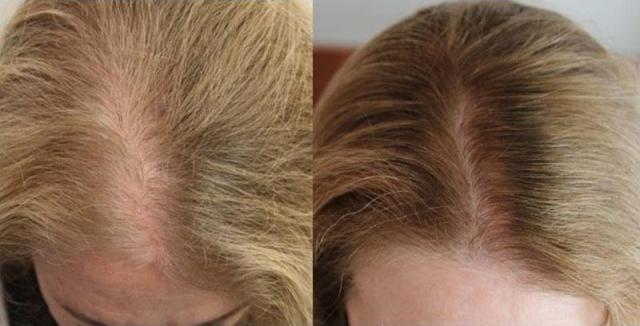
In addition, men typically have localized areas (patterns) of thinning, whilein women this usually occurs as thinning across the top, or over an even wider area. When women have very diffuse thinning over much of their scalp they are generally not good candidates for hair restoration surgery. However, women with localized hair loss, similar to the typical male pattern baldness, can successfully undergo hair restoration surgery.
Thinning hair in females is also characterized by an increase in the combination of normal thick hairs mixed in with finer, smaller hairs. This results in decreased density, and not total hair loss.
A woman's hair has also been proven to be more sensitive to the effects of stress than men's hair. Stress can result in hair loss in women and men. But this type of loss is not female pattern baldness. Rather, it is known as “telogen effluvium.” This type of hair loss is the shedding of hair in the resting phase when the body senses that it needs to divert its energies elsewhere. Therefore stress can temporarily changes the amount of hair that is shed. But the lost hair is likely to grow back.
The production of the hair loss-inducing androgens is also different among men and women. A woman produces a small quantity of androgens in the adrenal glands and the ovaries. The ovaries also produce pre-hormones, which are then converted to androgens on the outside of the ovaries or adrenal glands.
Generally speaking, a woman with hair loss will probably not experience total balding in a given area. But if there is total hair loss, this is most likely a sign of a previously hidden disease. For this reason, it’s important for females to have their hormone levels checked by a physician if they are experiencing heavy hair loss.
Finally, men and women react differently to various hair loss treatment options. In men, hair loss may be halted or even reversed by finasteride (brand named "Propecia"). However, Propecia is not safe for females or children. Minoxidil (Rogaine) can be effective for both men and women in treating hair loss.
However, for some women the causes of their hair loss are much more complex than the classic "male pattern baldness". Thus proper diagnosis of the underlying cause is vital before any hair loss treatments are attempted.
The following physicians are nationally well known experts in female hair loss. Feel free to contact them.
David Whiting in Dallas, Texas - 214 824-2087
Vera Price in San Francisco, California 415 353-4163
Maria Hordinsky in Minneapolis, Minnesota 612 625-1493
Wilma Bergfeld in Cleveland, Ohio 216 444-5722
For a web community that is dedicated to female hair loss visit HerAlopecia.com

Nizoral 2% is magnificent shampoo and a significant part of what's referred to commonly as the Big 3. The other two are the FDA approved and proven treatments Propecia (finasteride)and Rogaine (minoxidil). To date, Nizoral is the only shampoo on the market that can make the unique claim that it's proven to stop the formation of DHT. Its active ingredient ketoconazoleat 2% concentration has proven to be a moderate DHT inhibitor and has growth stimulating properties about as effective as Rogaine 2%.
This product includes 2%, the highest concentration of the active ingredient ketoconazole. To view the clinical abstract proving the effectiveness of ketoconazole in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia, view "Ketoconazole as a hair loss treatment". There is also a less concentrated 1% of Nizoral. To learn more, visit Nizoral regular shampoo.
We strongly suggest using Nizoral shampoo in addition to other proven treatments. Nizoral should be used 2 or 3 times a week to avoid dry hair and a flakey scalp.
On the off days, you may want to consider rotating Nizoral with other excellent shampoos designed specifically for thinning hair. See the recommended treatments section below for other shampoos we recommend.
Men and women sometimes suffer from hair loss for different reasons. Thus, diagnosing its cause is necessary to facilitate and promote proper treatment.
Don't expect immediate results. It's recommended to use Nizoral in conjunction with other proven treatments for at least 6 to 12 months before determining its effectiveness. Documenting your progress with bi-monthly photos can help you determine whether or not Nizoral has been successful in helping you maintain existing hair.
To date, only surgical hair restoration is proven to grow hair in completely bald areas. You are invited to have a free virtual consultation with one of our prescreened hair restoration physicians.
These types of treatments work by stimulating hair growth. However, they can't stop hair loss completely as they don't address the root causes of hair loss. Products that act to stimulate hair growth include Rogaine, Tricomin, Folligen, Proxiphen (along with Prox-N and Nano Shampoo) and Retin-A.

Tricomin, which is used by men and women, is a topical spray that has undergone a wide variety of scientific testing. The spray’s main ingredient is copper, which has been proven to be beneficial for hair.
The FDA has conducted some clinical studies, with the subjects applying the treatment twice per day for 24 weeks. These results were shown to be very positive. However, the product’s parent company, ProCyte Corporation, chose to release Tricomin as a cosmetic. They wanted to avoid the FDA approval process, which tends to be very lengthy.
Tricomin may be an effective option for those who want a treatment that’s undergone scientific testing, yet isn’t drug-based.
The product can be used safely by men, women and children. It’s also non-irritating and has no known side effects. Tricomin can be used for any type of hair loss
The product should be sprayed to damp or dry hair twice each day. But if you’re using another topical treatment, such as Rogaine, you should wait a few hours before applying Tricomin. This is because the scalp may turn a greenish color when mixed with other products. However, this discoloration isn’t permanent and washes out. And like other treatments, Tricomin needs to be used regularly to maintain its results.
Besides the spray, Tricomin is available as a shampoo and conditioner. They should be used as an addition and not as a replacement, though.
For more detailed information of Tricomin Follicle Therapy Spray, Shampoo and Conditioner, click here.

The makers of Tricomin make this product, available as a cream, lotion and spray. It was originally designed as a skin repair cream in the Dermatology Department at the University of California at San Francisco.
However, a 41-year-old woman with severe hair loss re-grew lost hair in two and one-half months with the cream. The company, Skin Biology, has since marketed this cream, which also contains copper-peptide as a hair loss treatment. The blue-colored copper-peptide complexes are meant to improve hair vitality and the health of the scalp and hair follicles.
Folligen products are meant for both men and women. They feature a cream for hairline application, spray for overall use, and lotion for bald spots. While Folligen may work on its own, its best results may be seen when it’s used with products like Rogaine.
Essentially, Folligen’s products soothe irritated scalps. They also relieve the itching and burning associated with Rogaine. However, the Folligen spray may cause itching or burning. Also, because the cream and lotion are bright green, it’s better to use them at night, while covering your pillow.
And while you can wash Folligen off easily, it’s not advisable for people with very light blonde hair to use the product. They may develop a greenish tinge to their hair.
Proxiphen is a prescription formula topical cream that has not yet received FDA approval. It combines the power of minoxidil and other chemicals. The cream should be applied everyday for the first 8 - 12 months, and after that, every other day. Proxiphen is dispensed only when a physician gives a diagnosis of hair loss.
Proxiphen-N, the non-prescription Proxiphen is less expensive and is also not as strong. It’s advisable for patients to use minoxidil with Proxiphen-N.
NANO (nicotinic acid N-Oxide) shampoos and conditioners are an excellent compliment to your existing minoxidil treatment. They contain NANO, which is a minoxidil-like hair growth stimulator. They also have agents that stimulate hair growth. These products are beneficial when used with Proxiphen and Proxiphen-N.
In order to see some results, Proxiphen-N and the NANO products need to be diligently used for at least 8-10 months at the very least.
A one-month supply at prescription strength is about $100. A 2-month supply of Proxiphen - N will cost $59.95. A 90-day supply of NANO Shampoo and Conditioner will cost $39.95 and $29.95, respectively.
Retin-A (also known by its scientific name, tretinoin gel 0.1%), is a topical treatment that’s primarily used as an acne medication. However, research has shown that Retin-A, either by itself or with Rogaine, may grow some hair in those with male pattern baldness or female pattern baldness.
To use Retin-A, you should apply a thin layer with a gauze pad or cotton swab to the affected areas at bedtime. Remember to wash your hands immediately after using the product! You should also take care not to get any Retin-A near the eyes, mouth, or open cuts. The medication may irritate sensitive skin.
It should also be mentioned that if Retin-A is used more often, the results will not improve. Rather, the side effects may increase. These effects include an immediate warming of the skin. Other skin problems may include peeling, itching, scaling, redness and maybe mild stinging. Luckily, once your skin adjusts to the medication, these effects should subside.
Retin-A may also cause increased sensitivity to sunlight as well as wind and cold. For these reasons, you should avoid prolonged exposure to the sun and sunlamps. You should also use effective sunscreens, and wear protective clothing.
In regards to pregnant mothers, research hasn’t shown any risk of birth defects, as of yet. Nevertheless, physicians recommend using Retin-A during pregnancy only if necessary. You should also consult your doctor before breast-feeding. One tube of Retin-A Cream can be purchased for about $28.00.
Click to learn more about Superoxide Dismutase (SOD's)